Honored and grateful to have been a guest of Paul’s Security Weekly #568
Category Archives: History
Meat is Murder on the Environment
After decades of seeing activists lay out the obvious economics of meat, and reading research by economists confirming the obvious, it looks as if the market finally is shifting. Eating meat is by far the number one impact to climate change and executives are starting to execute on the meatless menu, as you will see in a minute.
It always has seemed weird to me that if you wanted to remove meat from your work meals, or airplanes for that matter, you had to check a special box. Really it should be the other way around. If someone wants to add meat, let them be the “special” case.

I suppose executive dinners and board meetings should have something like this:
please check box if you want a major global catastrophic impact from your meal
Makes little to no sense to have meat automatically, and people should have to choose to accelerate global destruction, rather than set it as the mindless default.
Let me be clear here. I’m not saying I would never check the box. I’m not saying there would never be need for meat. I would always want the default to be meatless. When I say make it rare I mean it both ways. The economics of why are obvious, as I will probably say continuously and forever.
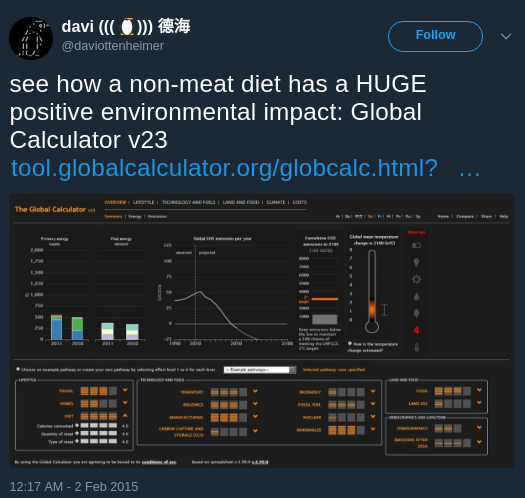
For example, years ago I was running the “Global Calculator” created for economic modeling, and reducing meat consumption undeniably had more impact than any other factors.
The Global Calculator is a model of the world’s energy, land and food systems to 2050. It allows you to explore the world’s options for tackling climate change and see how they all add up. With the Calculator, you can find out whether everyone can have a good lifestyle while also tackling climate change.
A sad and ironic side note here is the fact that meat consumption is the top factor in the “extinction crisis“, as 3/4 of earth’s animal population is disappearing at an alarming rate.
- climate change
- agriculture
- poaching
- pollution
- disease
I think it still may be counter-intuitive for a lot of folks when they hear they should stop eating meat to reduce climate change to prevent extinction of animals.
If you really like meat you will eat it rarely. Get it?
Thus a logical approach to solving many of the expensive problems people face today and into the future is to limit meat consumption within commercial space, because that’s where some expansive top-down decisions easily are made.
Imagine Google removing meat from its school-lunch-like program for its school-campus-like facilities for its school-children-like staff running its school-peer-review-like search engine. Alas, that probably means real executive leadership (not exactly what you get with kids trying to stay in school forever) where someone issues a simple order to reflect a principled stand (pun intended).
The first step on this path really should be Mar-a-Lago converts to vegan-only menus and becomes a research center for climate change, but I digress…
Instead it looks like Wework is the first apparently to be woke, as it has removed meat from its menus.
…told its 6,000 global staff that they will no longer be able to expense meals including meat, and that it won’t pay for any red meat, poultry or pork at WeWork events. In an email to employees this week outlining the new policy, co-founder Miguel McKelvey said the firm’s upcoming internal “Summer Camp” retreat would offer no meat options for attendees.
“New research indicates that avoiding meat is one of the biggest things an individual can do to reduce their personal environmental impact,” said McKelvey in the memo, “even more than switching to a hybrid car.”
It’s crazy to me that someone is calling out new research here when there is so much legacy work, but I guess that covers the question why they waited so long to do the right thing.
And just in case any of the typical extremist right-wing tech professionals (Shout out to the 303!) read this blog post, I offer this tasty morsel on vaccinating the mind against climate change falsehoods:
To find the most compelling climate change falsehood currently influencing public opinion, van der Linden and colleagues tested popular statements from corners of the internet on a nationally representative sample of US citizens, with each one rated for familiarity and persuasiveness.
The winner: the assertion that there is no consensus among scientists, apparently supported by the Oregon Global Warming Petition Project. This website claims to hold a petition signed by “over 31,000 American scientists” stating there is no evidence that human CO2 release will cause climate change.
The study also used the accurate statement that “97% of scientists agree on manmade climate change”. Prior work by van der Linden has shown this fact about scientific consensus is an effective ‘gateway’ for public acceptance of climate change.
Bring out the facts! I’ve noticed security professionals often ignore climate change harm and need facts as a gateway to accept that there are risks. Maybe a good time to drop facts on these self-proclaimed risk management elites is when they head to Las Vegas this summer…observe them carelessly gorging on meat while claiming to care about threats to their environment, and hand them an invite them to an exclusive WeWork party.
Cars Are Just Primitive Aristocratic Exoskeletons
The “carriage” form-factor is ancient.
So even though today we say “car” instead of carriage, we should know that to augment a single person’s travel with a giant opulent box is primitive thinking, and obviously doesn’t scale well to meet modern transit needs. Study after study by design experts have shown us how illogical it is to continue to build and use cars:

Fortunately, modern exoskeletons are more suited (no pun intended) to the flexibility of both the traveler and those around. Rex is a good example of why some data scientists are spending their entire career trying to unravel “gait” in order analyse and improve the “signature” of human movement. They discuss here how they are improving mobility for augmentation of a particular target audience:
This is an early-stage and yet it still shows us how wrong it is to use a car. When I expand such technology use to everyone I imagine people putting on a pair of auto-trousers to jog 10 miles at 20 mph to “commute” while exercising, or to lift rubble off people for 12 hours without breaks after an earthquake, or both.
We already see this class of power-assist augmented travel in tiny form-factors in the latest generation of electric bicycles, like the Shimano e8000 motor. It adds power as a cyclist pedals, creating a mixed-drive model:
For what it’s worth, the “gait” (wobble) of bicycles also is super complicated and a rich area of data science research. Robots fail miserably (nice try Yamaha) to emulate the nuance of controlling/driving two-wheels. Anyone saying driverless cars will reduce deaths isn’t looking at why driverless cars are more likely than human drivers to crash into pedestrians and cyclists. Any human can ride a bicycle, but to a driverless car this prediction tree is an impenetrable puzzle:

Unlike sitting in a cage, the possibilities of micro-engines form-fitted to the human body are seemingly endless, just like the branches in that tree. So it makes less and less sense for anyone to want cages for personal transit, unless they’re trying to make a forceful statement by taking up shared space to deny freedom to others.

What is missing in the above sequence of photos? One where cars are completely gone, like bell-bottom trousers, because they waste so much for so little gain, lowering quality of life for everyone involved.
Floating around in a giant private box really is a status thing, when you think about it. It’s a poorly thought out exoskeleton, like a massive blow-up suit or fluffy dress that everyone has to clean up after (and avoid being hit by).
Driverless cars meant to increase the number of empty carriages on roads (“summon mode”) will be like hell on earth. A gridlock of empty, unnecessary, wasteful “hackney” rides like failed 1700s aristocracy taught us nothing.
Here’s some excellent perspective on the stupidity of carrying forward the carriage design into modern transit:
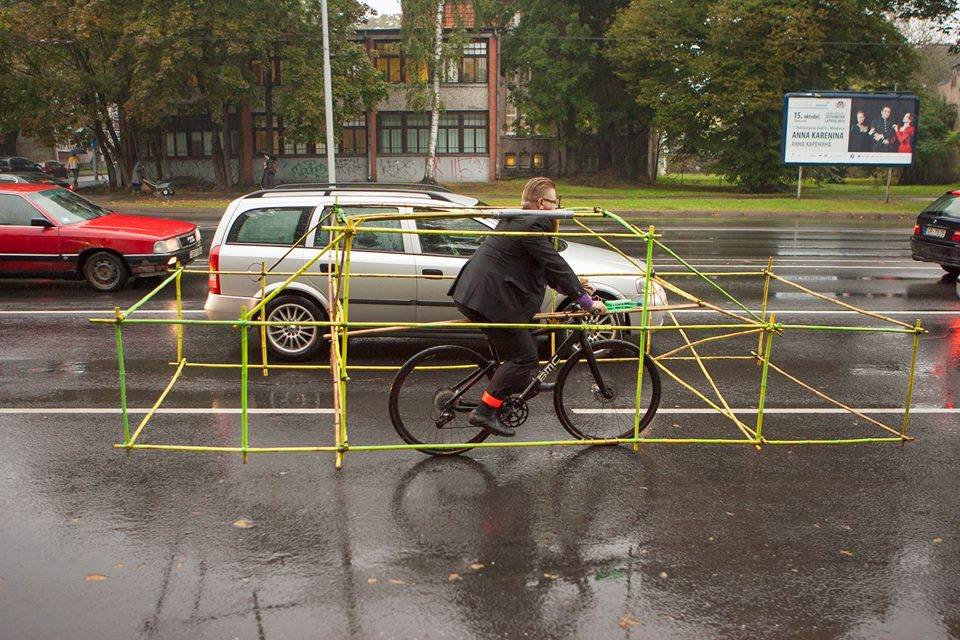


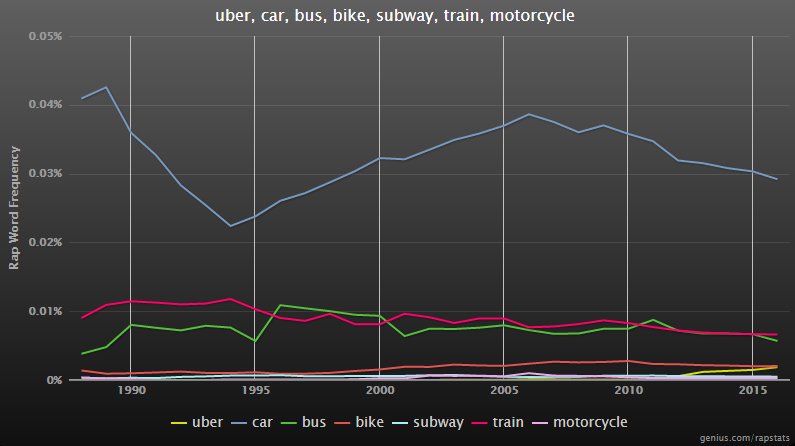
Rapstatus tells us cars still get a lot of lip service so I suspect we’re a long way from carriages being relegated to ancient history, where they belong.
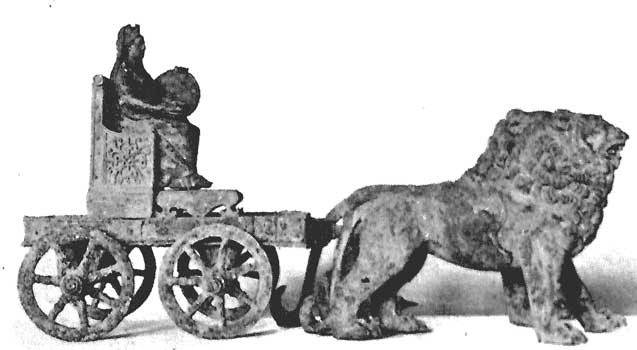
Nontheless I’m told new generations aren’t yet sold on dreams of long dead kings, and so I hope already they visualize something like this display of stupidity when asked if they would like their “AI assistant” (servant) to bring their carriage around…

This Day in History: Gettysburg Shoes
July 1st marks the beginning of a Civil War battle that many historians say is one of the most pivotal. And, as many historians also like to note, a love of pillaging Americans for their shoes supposedly is what drew pro-slavery forces arrogantly into Gettysburg on this date.
This topic of shaking-down hardworking Americans for their shoes is tied to General A. P. Hill. The man was a wealthy elitist who expected things for free (see also: slavery) and eagerly had abandoned his appointment in the U.S. Army to fight against freedom. To put it simply, Hill was committed to the violent expansion of slavery long after the practice had been abolished around the world.
Two decades before Hill was born, in 1807 the English already had abolished its slave trade. The idea of slavery became so unjustifiable in English society that by “1824 there were more than 200 branches of the Anti-Slavery Society in Britain“. No surprise then the agrarian state of New York abolished slavery 1827, England emancipated slaves in 1833, English Colonies 1838…but I’m getting ahead of myself here.
Mary Wollstonecraft, credited with helping found modern British feminist ethics, famously wrote against slavery in 1792:
Is sugar always to be produced by vital blood? Is one half of the human species, like the poor African slaves, to be subject to prejudices that brutalise them, when principles would be a surer guard, only to sweeten the cup of man? Is not this indirectly to deny woman reason?
Wollstonecraft’s sentiment was shared in the colonies, believe it or not, and thus we see examples like the agrarian colony of New York debating how to expedite emancipation, two decades earlier than Wollstonecraft’s call for a boycott on slave-made goods:
Most of the Revolutionary leaders who came to power in New York in 1777 had anti-slavery sentiments, yet, as elsewhere in the North, the urgency of the war with Britain made them delay, and they restricted their activity to a policy statement and an appeal to future legislatures “to take the most effective measures consistent with public safety for abolishing domestic slavery.” This resolution passed in the state Constitutional Convention by a vote of 29 to 5.
Note the five dissenters. Obviously some in the 1700s were not quite convinced. And so by 1861 we have a treasonous General A. P. Hill taking up arms against his own country. In a nutshell, many white elitist men in America did not want to do hard work and believed their easy/lazy lives and financial inheritances (see also: people treated as property to be bought and sold) were threatened unless they could continue to enslave Americans and steal their goods.
Today you may be surprised to see the U.S. Army has named a fort after an infamously treasonous and foolish man like A. P. Hill. Given that he dedicated his life to killing American soldiers for personal profit, who thought this made any sense?
The installation was named in honor of Lt. Gen. Ambrose Powell Hill, a Virginia native who distinguished himself…
Please take special note of the fact that the U.S. Army doesn’t call the person they are honoring an American, because his treason to preserve slavery by killing Americans, killed his citizenship.
Also nice try U.S. Army with your Virginia reference. Obviously Hill was far from being a true native of Virginia.
That being said I must agree with the second part of the sentence, this treasonous man hateful of his own country certainly distinguished himself. The U.S. Army doesn’t mention it but his impatience, as well as lust for plundering Americans and putting people in chains, may have led to one of the greatest tactical blunders in U.S. military history. So distinguishable.
Also he contracted gonorrhea while a cadet at West Point, screwed around so much he graduated late, and became known for taking “sick leave” right in the heat of any major battle.
Now, to be fair to Hill being so distinguished, I must admit he shared poor decision-making with his pro-slavery General Heth on June 30th, 1863. Heth had ordered his pro-slavery General Pettigrew to enter Gettysburg and ransack it. Pettigrew had followed these orders at first but turned tail after he observed American cavalry and infantry already near the town.
In “The Civil War: A Narrative” there’s a scene where Hill approaches Heth and hears of Pettigrew’s reluctance. Hill, our man of the hour, then insists to Heth there can be no significant American forces present.
OOPS.
The narrative tells us Heth obediently then sends his Pettigrew back once again to plunder Gettysburg and “get those shoes!”

Narratives aside, by 5AM on July 1st, as Heth himself approached Gettysburg to damage it, he realized Pettigrew had been right, Hill was stupidly wrong, and significant numbers of American forces were present. Yet even that didn’t dissuade Heth, who continued ordering Pettigrew to march on.
Hill’s insistence that he conferred with Lee and there would be no resistance to plunder seems to be the real story here, shoes or not. There was an inherent desperation of Lee and his pro-slavery men to plunder America (see also: slavery), which on this particular day began the largest land battle in the western hemisphere, lasting 3 days and killing nearly 50,000 people, to the disadvantage of pro-slavery forces.
One of the stranger footnotes (no pun intended) to this story is that while Gettysburg had a lot of American forces defending freedom, it didn’t have any shoes.
These pro-slavery Generals, all of them, not only chose to be blind to the evils of slavery, they also were blind on two more levels. A particularly inhumane General with the ironic name of Early (infamous for helping to invent the “Lost Cause” view) had tried to pillage Gettysburg days before Heth had set his sights on it.
This means Americans living in Gettysburg already had been subjected to pro-slavery militia demanding ransom in 1,000 shoes and attacking the town.
No shoes were found, as you can plainly read here:

Had there been any shoes, they might have been the standard issue “Jefferson Boots”, named after Thomas Jefferson who is thought to have created an American fad for French ankle-high laced shoes by wearing them instead of previously common English ones with large buckles.

However, again I must say, NO SHOES IN GETTYSBURG.
So for those historians arguing pro-slavery forces really centered their offensive on shoes, maybe put a sock in it.
Is there any evidence that pro-slavery General Early told others that the town couldn’t cough up any Jefferson boots despite his violent demands? Lee and Hill both supposedly had scouts relaying information but perhaps it wouldn’t have made any difference what Early said, given how Pettigrew was rebuffed when he tried to explain the dangers of trying to plunder Americans on this day.
To put this in perspective, it’s not like in the days leading up to the Gettysburg battle someone could tell Lee or Hill that slavery is unjustified and they would listen; if these men wanted stealing to be in their plans, they were going to threaten and kill Americans until some damn things to steal were found or everyone was dead for refusing to see things the pro-slavery way.
Again, Hill quit the U.S. Army to plunder America in the most unjustified way to retain elite status. In that sense Gettysburg was simply another day of plunder to Hill and his men, whether stealing goods, separating babies from mothers, or perpetuating slavery to improve his own status at the expense of others.
Within three days pro-slavery forces had been destroyed at Gettysburg, which helped signal an end to their plans to use violence against fellow citizens to expand slavery practices into western territories (what the war was really about); 60 years after England had abolished slavery, and 30 years after slaves in America (if still colonies) would have been emancipated, the self-proclaimed “elite” white supremacists fighting to perpetuate obviously tyrannical practices of their former King were defeated (pun not intended).
Also, just as one final footnote, I think it is time for the U.S. Army to officially remove honors to Hill. I say that not only because Hill was a murderous traitor and terror to Americans, but also because we could say he finally got the boot he so desired.