Executive summary: Soviet advances opened Japan to surrender, and NOT the atomic bomb. The best and most logical explanation relates directly to Stalin’s commitment he would enter the Pacific War three months after the surrender of Nazi Germany, as he had promised Allied leaders. The 1945 atomic bomb was a distraction, had little effect versus a reality of Stalin’s forces threatening to completely and quickly overrun Japan. Perhaps at best the bomb provoked the Soviets to get there before everything was destroyed (already 68 cites in Japan had been completely burned to the ground by months of napalm such that targets for atomic bombs had to be the somewhat unknown and insignificant cities — the only places still standing). The Soviets started to roll over Manchuria so quickly that in only a couple of weeks the thoughts of negotiated peace evaporated. Abruptly losing in a few months most of the territory they had conquered over the entire war, and facing a very real possibility of Russians walking onto Japanese mainland, Japanese peace factions rushed towards quitting the war and military leaders wilted.
Long form: The usual story told in American history classes is that dropping two atomic bombs on Japan saved American lives. This is mostly false. There was no reason for America to invade and the country had lost its air force, navy and even resources like oil to defend itself.
Military leaders like MacArthur, Nimitz, Eisenhower, even Patton opposed use of the atomic bomb so there was little to no truth to any invasion casualty concern claims. The Soviet Union in fact was quickly en route to rout Japan on land, sustaining minimal casualties with huge gains.
Studies now show the opposite kind of analysis, that the atomic bombs killed more Americans than if Japan had been invaded on land. Nearly as many Americans died from nuclear radiation and fallout during development of the bombs as the number of Japanese who died from the bombs being dropped.

One might still argue soldiers at that time had two bombs doing the hard work for them and reducing risk, even if Americans were killed at shockingly high rates for decades afterwards.
The problem with this theory is these atomic bombs didn’t force surrender, thus didn’t directly replace the purpose of a land invasion.
Nonetheless a story told in America has been that dropping two bombs on Japan proved to them such a level of superiority in warfare (“assured destruction”), it somehow suddenly compelled the Japanese to immediately give up… not to mention a story also told that atomic bombs held the Soviets at bay afterwards.
All this unfortunately is false history (see “Hidden Hot Battle Lessons of Cold War“, for additional perspective).
Here is Truman’s famous June 1st, 1945 speech calling on Japan to surrender, just to set the context of what the public was hearing at the time:
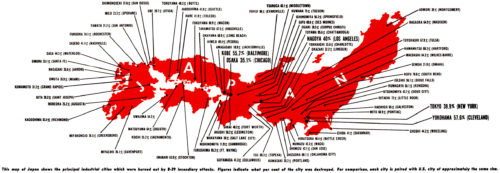
Take note that the warning was after massive bombing campaigns like March 9-10, 1945 where some 330 B-29 bombers burned 40 square miles of wood-built Tokyo to the ground killing over 100,000 civilians.

However Japan didn’t fear civilian casualty loads and couldn’t have really understood at the time why this new bomb mattered in August after a long summer of entire cities being destroyed. In a chillingly ironic manner US military leaders also didn’t fear civilian casualties.

Japanese leaders instead greatly feared Soviet declaration of war on them. They thought Stalin’s shift to formal enemy would very negatively alter the terms of surrender (Soviets no longer would mediate a surrender that Japan had been asking about for weeks before the bombs were dropped).
I don’t write these things to be provocative, rather to help us better educate people about the past and also to plan for the future. Perpetuating a false narrative doesn’t do America any favors. And most of what I’m writing here is old news.
In 2013 for example Foreign Policy published “The Bomb Didn’t Beat Japan … Stalin Did”
Japanese historians contended it was the USSR declaring war against Japan that convinced their Emperor and gov that surrender was the only option.
In fact American propaganda dropped into Japan at that time (translated here to English) emphasized the Red Army invading, a “ring of steel” approaching with no mention of bombs at all.

Japan referred to atomic bombs like a “single drop of rain in the midst of a hurricane”, given that they already had seen months-long fire-bomb raids of Tokyo that left it over 50% destroyed with 300,000 burned alive and 750,000 injured.
The reason Tokyo wasn’t targeted with atomic bombs was it was too destroyed already — atomic effect wouldn’t have been measurable (125,000 were killed in atomic attacks on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, which would mean it was similar in effect or even less than a single night of the fire bomb raids hitting Tokyo for months)
Two years before the Foreign Policy piece, a 2011 article in Boston papers offered the following insightful analysis in “Why did Japan surrender?”
“Hasegawa has changed my mind,” says Richard Rhodes, the Pulitzer Prize-winning author of “The Making of the Atomic Bomb.” “The Japanese decision to surrender was not driven by the two bombings.” […] “The bomb – horrific as it was – was not as special as Americans have always imagined. …more than 60 of Japan’s cities had been substantially destroyed by the time of the Hiroshima attack, according to a 2007 International Security article by Wilson, who is a senior fellow at the Center for Nonproliferation Studies at the Monterey Institute of International Studies. In the three weeks before Hiroshima, Wilson writes, 25 cities were heavily bombed. To us, then, Hiroshima was unique, and the move to atomic weaponry was a great leap, military and moral. But Hasegawa argues the change was incremental. “Once we had accepted strategic bombing as an acceptable weapon of war, the atomic bomb was a very small step,” he says. To Japan’s leaders, Hiroshima was yet another population center leveled, albeit in a novel way. If they didn’t surrender after Tokyo, they weren’t going to after Hiroshima.
It’s very hard to argue with these common sense points. Massive civilian casualties were mounting and having little effect. Did novelty of a bomb that was a secret suddenly change minds? Even common sense would say no, and the historical record increasingly confirms this.
Or as DW puts it in their documentary, why did American drop a second bomb on Nagasaki if that Hiroshima one supposedly could send a message to surrender?
Video F18ODD8YyuE deleted from YouTube
Or here’s the BBC “accounts of American justification” for dropping a second bomb.
Civilian suffering had never coerced Tokyo to change tactics, and these bombs also failed in that sense. Hiroshima was the 69th city in Japan destroyed by bombing and Nagasaki wasn’t even the primary target (chosen after primary target had unfavorable weather) so it was destroyed just for the sake of bombing someplace at all.
In the end, America dropped these bombs most probably to see what the effects of dropping atomic bombs would be (expressed in the now deleted DW video above as “…my mother fell apart like dry sand when I touched her foot…”) and then the US Air Force created a supporting narrative to justify continuing the program.
Historians have been trying to explain the false stories away ever since.